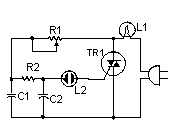
Triac temperature sensitive heater control

Triac temperature-sensitive heater control. This circuit can be modified to control a motor with a constant load. While the circuit is designed for heating applications, it can also be adapted for cooling by interchanging RT and R2 (courtesy of Motorola Semiconductor Products Inc.).
The described circuit utilizes a triac to regulate temperature-sensitive heating elements by controlling the power delivered to them. The triac functions as a switch that can be turned on and off rapidly, allowing for precise control over the heater's output. The temperature sensing is typically achieved using a thermistor or a thermocouple, which provides feedback to the control circuit based on the ambient temperature.
In the heating configuration, the circuit operates by monitoring the temperature and adjusting the conduction angle of the triac accordingly. As the temperature rises above a set threshold, the control circuit reduces the power to the heater to maintain the desired temperature. Conversely, when the temperature drops below the threshold, the control circuit increases the power, allowing the heater to operate at full capacity until the set point is reached again.
When modified for motor control, the same principles apply. The circuit can be adapted to control the speed of a motor with a constant load by adjusting the power delivered to the motor. This can be particularly useful in applications where precise speed control is necessary, such as in fans or pumps. The interchange of RT and R2 allows for the reconfiguration of the circuit, enabling it to switch from a heating application to a cooling application, thus providing versatility.
In both configurations, the circuit design must incorporate appropriate safety features, such as over-temperature protection and current limiting, to prevent damage to the components and ensure reliable operation. Additionally, proper heat sinking for the triac may be necessary to dissipate heat generated during operation, particularly in high-power applications.Triac temperature-sensitive heater control. This circuit can be modified as shown to control a motor with a constant load. As shown the circuit is for heating applications but can be used for cooling by interchanging RT and R2 (courtesy Motorola Semiconductor Products Inc. ). 🔗 External reference
The described circuit utilizes a triac to regulate temperature-sensitive heating elements by controlling the power delivered to them. The triac functions as a switch that can be turned on and off rapidly, allowing for precise control over the heater's output. The temperature sensing is typically achieved using a thermistor or a thermocouple, which provides feedback to the control circuit based on the ambient temperature.
In the heating configuration, the circuit operates by monitoring the temperature and adjusting the conduction angle of the triac accordingly. As the temperature rises above a set threshold, the control circuit reduces the power to the heater to maintain the desired temperature. Conversely, when the temperature drops below the threshold, the control circuit increases the power, allowing the heater to operate at full capacity until the set point is reached again.
When modified for motor control, the same principles apply. The circuit can be adapted to control the speed of a motor with a constant load by adjusting the power delivered to the motor. This can be particularly useful in applications where precise speed control is necessary, such as in fans or pumps. The interchange of RT and R2 allows for the reconfiguration of the circuit, enabling it to switch from a heating application to a cooling application, thus providing versatility.
In both configurations, the circuit design must incorporate appropriate safety features, such as over-temperature protection and current limiting, to prevent damage to the components and ensure reliable operation. Additionally, proper heat sinking for the triac may be necessary to dissipate heat generated during operation, particularly in high-power applications.Triac temperature-sensitive heater control. This circuit can be modified as shown to control a motor with a constant load. As shown the circuit is for heating applications but can be used for cooling by interchanging RT and R2 (courtesy Motorola Semiconductor Products Inc. ). 🔗 External reference